How Many BTUs Do You Need?
AUTHOR: FERRELLGAS
What is a “BTU?”
A BTU, or British Thermal Unit, is a standard measure of energy. It tells us how much energy is needed to heat or cool something. Specifically, one BTU equals the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
BTUs help us figure out how much propane your appliances or heating and cooling systems need to keep your home or workspace comfortable.
How BTU Impacts Energy Efficiency
Choosing a heating or cooling system with the right BTU rating can make a significant difference in how well it performs.
-
Save Energy: A properly sized system uses energy more efficiently.
-
Lower Bills: Using less energy keeps your utility bills lower.
-
Environmentally Friendly: Using only the energy you need helps lower your carbon footprint.
-
Better Comfort: The right system keeps your space cozy without overworking.
Calculating the Number of BTUs Needed to Heat an Area
To determine how many BTUs your space needs, you need to consider how much heating or cooling your space requires. This depends on:
-
The size of the space (square footage or cubic feet).
-
Your climate and how much the temperature needs to change.
-
Factors like insulation, windows, and sunlight.
Use This Formula to Calculate BTUs:
(Desired temperature change) × (cubic feet of space) × 0.133 = BTUs needed per hour
Example BTU Calculations
Let’s say you’re heating a garage:
-
It’s 1,000 square feet with an 8-foot ceiling, so the space is 8,000 cubic feet.
-
The outside temperature is 30°F, and you want it to be 70°F inside. The temperature change is 40°F.
Now, plug the numbers into the formula:
40°F × 8,000 cubic feet × 0.133 = 42,560 BTUs per hour.
That’s how many BTUs your heating system needs to keep the garage warm.
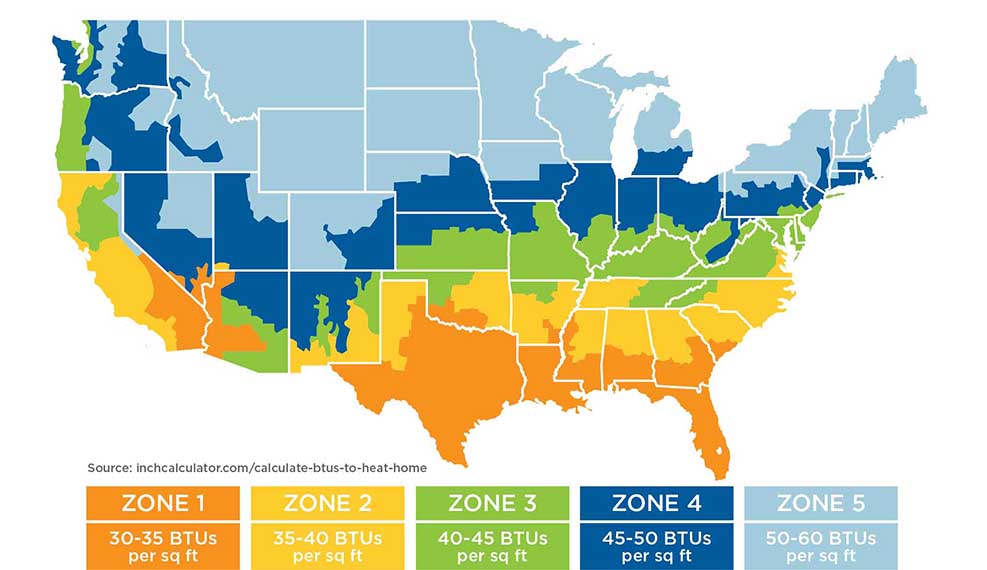
What Factors Determine How Much BTUs You Need?
From the climate you live in, to the size and design of your space, several factors play a role in determining how much heating or cooling power is required for a space.
1. CLIMATE AND WEATHER
Your geographic location plays a big role in your BTU needs.
-
Warmer areas (Zone 1 or 2): 30–40 BTUs per square foot.
-
Moderate areas (Zone 3 or 4): 40–45 BTUs per square foot.
-
Colder areas (Zone 5): Up to 60 BTUs per square foot.
2. AVERAGE SQUARE AND CUBIC FOOTAGE
Naturally, the bigger the space, the bigger the need, but don’t fall into the bigger is better trap. Purchasing an oversized heater or air conditioner creates a different set of concerns, such as:
-
Turning on and off too often can cause undue wear and tear.
-
Creates excessive Noise.
-
Wastes energy.
-
Costs more to run.
Using the above formula helps you size your system correctly.
3. BUILDING MATERIAL AND QUALITY
The way your home is built also affects how many BTUs you need:
-
Windows: More windows require higher heating/cooling capacity.
-
Insulation: Poor insulation demands more BTUs.
-
Sunlight: South-facing windows can heat up a room quickly, requiring more cooling power.
For an accurate assessment, consult an HVAC professional who can account for insulation, layout, and other factors.
Interested in powering your heating with propane?
Propane is an excellent choice for anyone looking to power their home or business more efficiently. If you're considering making the switch, contact Ferrellgas to speak to one of our friendly, knowledgeable experts.
Sources
BTU Calculator (Heating) - How Many BTUs Do I Need for a Room?, We Love Fire
How Many BTU Per Square Foot Do I Need?, HVAC Alliance Expert
Units and calculators explained, U.S. Energy Information Administration
CATEGORIES
Archives
- Winter 2025
- Fall 2025
- Summer 2025
- Spring 2025
- Winter 2024
- Fall 2024
- Summer 2024
- Spring 2024
- Winter 2023
- Fall 2023
- Summer 2023
- Spring 2023
- Winter 2022
- Fall 2022
- Summer 2022
- Spring 2022
- Winter 2021
- Fall 2021
- Summer 2021
- Spring 2021
- Winter 2020
- Fall 2020
- Summer 2020
- Spring 2020
- Winter 2019
- Fall 2019
- Summer 2019
- Spring 2019
- Winter 2018
- Fall 2018
- Summer 2018
- Spring 2018
- Winter 2017
